Part 5: Transform Data to Use MDX
Introduction
In Part 4, you used the gatsby-source-filesystem source plugin to build a Blog page that lists the names of your blog post files. But you weren’t able to actually render the contents of your post files, because gatsby-source-filesystem doesn’t provide a field for it. To do that, you’ll need another type of plugin called a transformer plugin.
Sometimes, the format of the data you get from source plugins isn’t exactly what you want to use to build your website. For example, the filesystem source plugin lets you query data about files, but it doesn’t let you use the data inside the files themselves. To make this possible, Gatsby supports transformer plugins, which take the raw content from source plugins and transform it into something more usable.
In this part of the Tutorial, you’ll learn about one particular transformer plugin, gatsby-plugin-mdx, which lets you use MDX, a file format that allows Markdown and JSX alongside your text content. (Fun fact: this Tutorial is actually written in MDX!) You’ll use MDX to add some content to your blog post files, and then you’ll use gatsby-plugin-mdx to render the contents of your posts on your Blog page.
Note: Usually, transformer plugin names start with gatsby-transformer-. (gatsby-plugin-mdx is one exception to this convention.)
To see a list of other transformer plugins, try searching for gatsby-transformer- in the Gatsby Plugin Library.
By the end of this part of the Tutorial, you will be able to:
- Write an MDX file with Markdown formatting and frontmatter.
- Use the
gatsby-plugin-mdxplugin to render the contents of your MDX files on your Blog page. - Use the
sortfield to control the order of results in your GraphQL queries.
Prefer a video?
If you’d rather follow along with a video, here’s a recording of a livestream that covers all the material for Part 5. Please note: At the time of recording an older version of gatsby-plugin-mdx was used and thus the video contents and text contents are different. Please always follow the written instructions. We’ll do our best to record a new version in the future, thanks for understanding!
Note: Parts of this recording may be slightly outdated, but the concepts are generally applicable. For the most up-to-date information, follow along with the written tutorial.
Don’t want to miss any future livestreams? Follow our Gatsby Twitch channel.
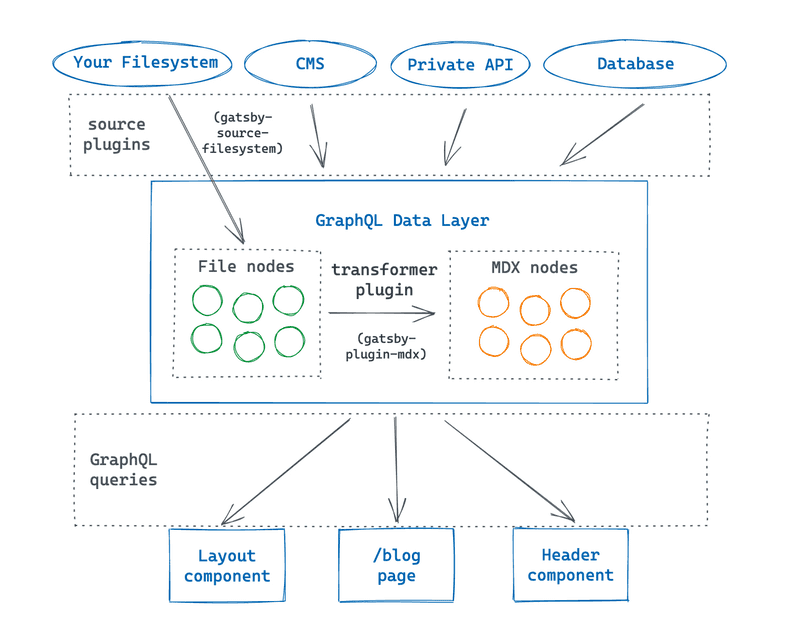
A closer look at Gatsby’s GraphQL data layer
To understand how gatsby-plugin-mdx and other transformer plugins work, you need to know a bit more about how Gatsby’s GraphQL data layer works.
Inside the data layer, information is stored in objects called nodes. A node is the smallest form unit of data in the data layer. Different source plugins create different types of nodes, each of which have their own properties. For example, gatsby-source-filesystem creates File nodes.
A transformer plugin converts nodes from one type to another. For example, the gatsby-plugin-mdx plugin transforms File nodes that have the .mdx extension into MDX nodes, which have a different set of fields that you can query using GraphQL. Transformer plugins let you manipulate the raw data in the nodes created by source plugins, so that you can get it into the structure or format you need.
Note: Even though it’s called a transformer plugin, it’s not actually changing the original nodes created by the source plugins. Each transformer plugin creates new nodes based on the data from the sourced nodes, but it doesn’t actually change the source nodes themselves. So even though gatsby-plugin-mdx creates new MDX nodes in the data layer, you can still access the original File nodes created by gatsby-source-filesystem.
In this part of the Tutorial, you’ll learn how to use a transformer plugin to create MDX nodes from your File nodes.
Add some MDX content to your blog posts
In Part 4, you created empty files for your blog posts. Now, it’s time to fill them in!
Using Markdown formatting in MDX
MDX files let you format text using Markdown, a markup language that uses a special syntax to add special formatting to your text elements. For example, you can make text appear strong by wrapping it in **double asterisks**, or you can create a link by using a syntax like [text to link](url).
Once you get used to what all the different symbols mean, Markdown can be easier to read than HTML, which makes it a popular format for written content like blog posts.
New to Markdown? The MDX documentation includes a table of components that shows the different formatting options available. It includes things like headings, blockquotes, lists, and code blocks.
Frontmatter
With gatsby-plugin-mdx, you can also add frontmatter to your MDX files. Frontmatter is additional metadata about your file. It won’t be rendered on your page, but it’s a way for you to add some extra details about your content. For example, you might store your post title or the date it was published.
To add frontmatter to your post, put it between an opening and closing set of three hyphens (---) at the top of your MDX file. Within the opening and closing hyphens, you can create key-value pairs for any kind of data you want to store about your file.
Here’s an example:
You’ll learn more about how to access the frontmatter for your posts later on.
Add some Markdown content to each of the .mdx files you created in your /blog directory in Part 4.
Include frontmatter with fields for the title of each post, the date it was published, and a slug. The slug will be used to construct the final URL of each post. Give each post a different date, to make it easier to add sorting later on. After the frontmatter, write some post content using some Markdown syntax.
Here are some example posts that you can use for inspiration:
Render each post’s contents on the Blog page
Now that you have some MDX content inside your blog posts, it’s time set up the gatsby-plugin-mdx transformer plugin.
Quick Refresher: Remember the process for adding a plugin to your site (from Part 3)? See if you can remember the three steps from memory before checking your answer. (Science has shown that the act of trying to actively recall information helps you retain it better!)
The gatsby-plugin-mdx plugin provides the allMdx and mdx fields for your GraphQL queries.
To render your posts on the Blog page, you’ll complete a few different steps:
- Install and configure the
gatsby-plugin-mdxtransformer plugin and its dependencies. - Update the Blog page query to use the
allMdxfield fromgatsby-plugin-mdxinstead ofallFile. - Render your post’s excerpt in your Blog page.
Task: Install and configure the MDX transformer plugin (and dependencies)
The gatsby-plugin-mdx package requires a one additional dependencies to run: @mdx-js/react which maps the MDX implementation to React components.
In your terminal, run the command below to install
gatsby-plugin-mdxand its dependencies. (This adds all two packages to thedependenciesobject in yourpackage.jsonfile and to yournode_modulesdirectory.)Add
gatsby-plugin-mdxto thepluginsarray in yourgatsby-config.jsfile, so that Gatsby knows to use the plugin when building your site.
Tip: There are a variety of remark plugins that you can use to add extra features to your Markdown. You can configure them using the gatsbyRemarkPlugins option when you configure gatsby-plugin-mdx in your gatsby-config.js file.
Here are some popular remark plugins:
gatsby-remark-images: Use this if you want to generate responsive images when using the Markdown image syntax (which looks like this:).- To use this plugin, you’ll also need
gatsby-plugin-sharp, which you installed already in Part 3.
- To use this plugin, you’ll also need
gatsby-remark-prismjs: Add syntax highlighting to your code blocks.gatsby-remark-autolink-headers: Automatically create links for all the headers in your Markdown content.
Try searching for gatsby-remark- in the Gatsby Plugin Library for a full list.
Task: Update the Blog page query to use the allMdx field instead of allFile
The gatsby-plugin-mdx plugin makes two new fields available for you to use in your GraphQL queries: allMdx and mdx. In this part of the Tutorial, you’ll use allMdx to add the contents of each blog post to your Blog page. (You’ll use the mdx field later on, in Part 6.)
You can use the allMdx field to request data for multiple MDX nodes at once (similar to the way allFile worked with File nodes). Open GraphiQL and explore what fields are available on MDX nodes. Try running a few queries to see what kind of information you get back.
Quick Refresher: Remember how to access GraphiQL? See if you can remember the steps before checking for the answer in Part 4. (Check the section called “Use GraphiQL to explore the data layer and write GraphQL queries”).
Use GraphiQL to create a new query that gets data about your blog posts using the allMdx field instead of the allFile field.
- Under
allMdx, open thenodesdropdown. Inside thefrontmatterdropdown, you should see fields for all the keys you created in the frontmatter of your MDX files. Select thetitleanddatefields. You can use theformatStringargument on thedatefield to change the way your dates are displayed (see Syntax Hint below).
Syntax Hint: When it comes to using dates in your frontmatter, the formatString argument is a helpful tool for changing the way the date is displayed.
Imagine you have a key in your frontmatter with a value that uses a date format like "YYYY-MM-DD". (It doesn’t matter what you name the key, as long as the value has the required format.) GraphiQL will automatically detect that your value is a date, and when you select the corresponding frontmatter field in the Explorer pane, GraphiQL will automatically show a few arguments that you can pass to that field. One of those arguments is called formatString, which you can pass a Moment.js formatting token to change the way the date displays.
For example, if your MDX frontmatter looks like this:
…and your GraphQL query looks like this:
…then the dates in your response will look like this: "July 23, 2021".
While you’re at it, add the
idfield, which is a unique string that Gatsby automatically adds to every node in the data layer. (You’ll use this as a Reactkeylater on, when you iterate over your list of posts.)Execute your query by clicking the triangle button. Your response object should look something like this:
You might notice that your posts aren’t listed in order. Most blog sites list their posts in reverse-chronological order, so that the newest posts are listed first. You can sort the data nodes in your response by using the
sortargument on theallMdxfield.- In the Explorer pane, toggle the
sortdropdown underneath theallMdxfield. - Under
sort, check thefrontmatterargument, and use the dropdown to selectDESC. This will sort the nodes in descending order, so that the newest posts come first.
- In the Explorer pane, toggle the
Run your query again to verify that the posts come back in the correct order. Your response should look something like this:
The last thing you need to add to your query is a preview of each posts content! To do that, add the
excerptfield to your query.When you run your query, the
excerptfield for each node should look something like the data shown below.
Now that you have your GraphQL query all set up, it’s time to tackle the last piece of the puzzle: rendering your posts in the Blog page.
Pro Tip: When transformer plugins create a new node, they add a parent field that references back to the original source node it was created from. For example, when gatsby-plugin-mdx creates new MDX nodes, it adds a parent field which you can use to access data from the original File node.
Using the parent node can come in handy if you want to use data from the transformed nodes along with data from the original source nodes. For example, the query below gives you back the time a file was changed, which you could use to display when a post was last updated.
Task: Render your post’s excerpt in your Blog page
Now that your GraphQL query is all set up, it’s time to replace the page query in your Blog page component.
Start by swapping out the
allFilepage query in your Blog page for the one you just created usingallMdx. (Don’t forget to delete the query name!) And if you haven’t already from completing the task in Part 4, you’ll need to import thegraphqltag from thegatsbypackage.Next, update the JSX for your Blog page to use the data fields of your response. Start by rendering just the title and date for each post.
- Now that you’re rendering more than just a filename, it makes more sense to use the
<article>semantic HTML element instead of a<ul>and nested<li>elements. - You can also use the
idfield as your uniquekeyprop for each post. (React uses thekeyprop to keep track of what elements need to be re-rendered. If you don’t include it, you’ll get a warning in your browser console. For more on thekeyprop, check out the React Docs: List and Keys.)
- Now that you’re rendering more than just a filename, it makes more sense to use the
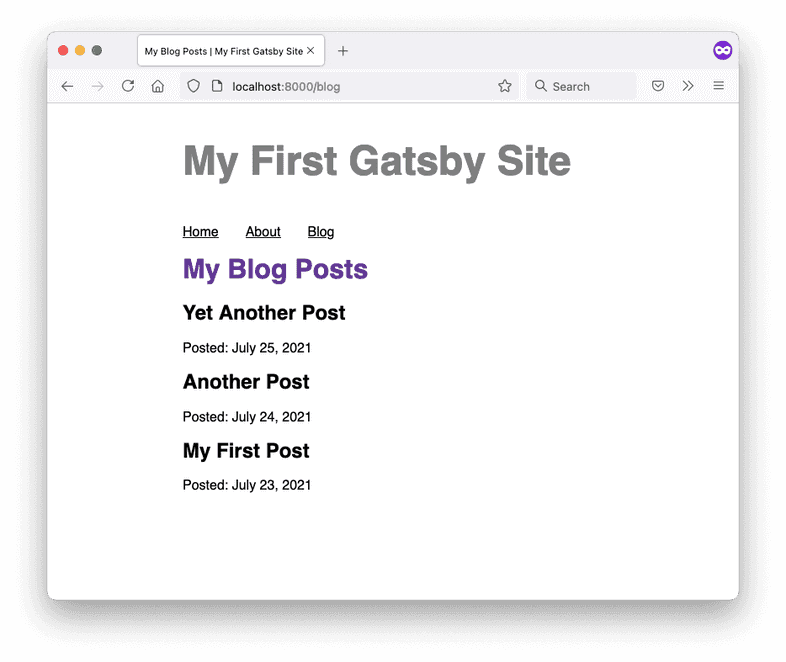
Go to
localhost:8000/blogin your web browser. You should be able to see the titles and dates for each of your posts:
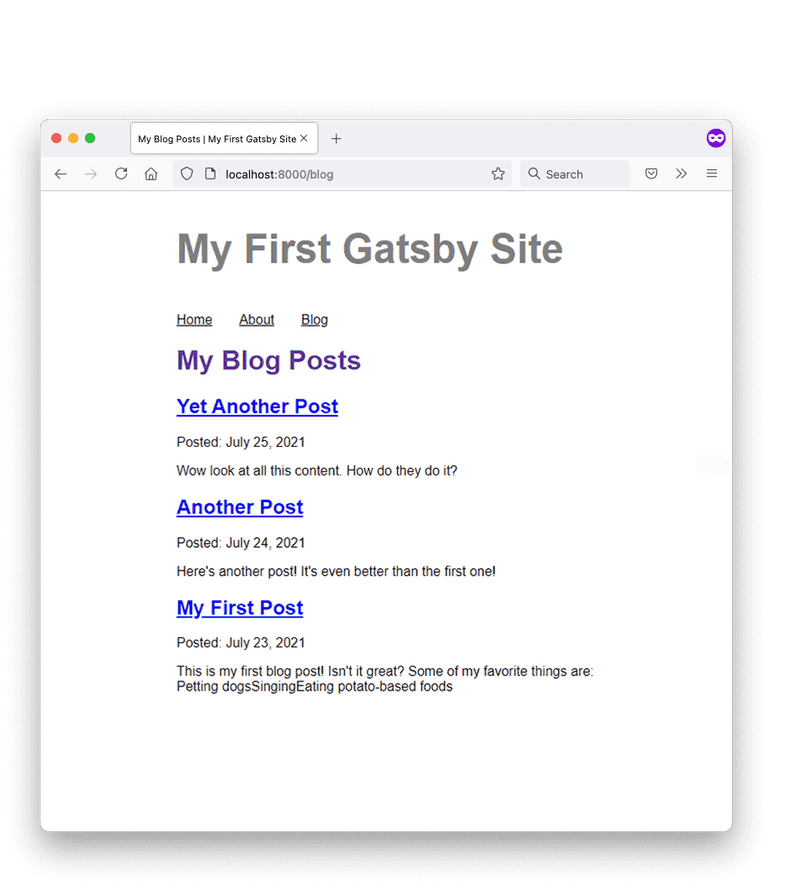
- The final step in this part of the Tutorial is to render the excerpt of your MDX blog posts. In the JSX for your Blog page render the value of the
excerptfield:
Note: The excerpt which is returned by the query doesn’t contain HTML tags so the unordered list for “My First Post” isn’t rendered correctly. But don’t worry, you are going to implement a better solution later.
Nice work! Your site now has a blog page with actual content.
Want to see how it all fits together? Check out the finished state of the GitHub repo for the example site.
Summary
Take a moment to think back on what you’ve learned so far. Challenge yourself to answer the following questions from memory:
- What is a transformer plugin? How do transformer plugins affect the data in the data layer?
- What is MDX? Why is it useful?
Ship It! 🚀
Before you move on, deploy your changes to your live site on Gatsby Cloud so that you can share your progress!
First, run the following commands in a terminal to push your changes to your GitHub repository. (Make sure you’re in the top-level directory for your Gatsby site!)
Once your changes have been pushed to GitHub, Gatsby Cloud should notice the update and rebuild and deploy the latest version of your site. (It may take a few minutes for your changes to be reflected on the live site. Watch your build’s progress from your Gatsby Cloud dashboard.)
Key takeaways
- Data in Gatsby’s GraphQL data layer is stored in nodes.
- Each source plugin creates a different type of node with different fields.
- Transformer plugins create new types of nodes, using data from existing source nodes as a starting point. Transformer plugins don’t actually change the original source nodes.
gatsby-plugin-mdxis a transformer plugin that lets you use MDX in your site. With MDX, you can create text content with Markdown formatting and embedded React components.
Share Your Feedback!
Our goal is for this Tutorial to be helpful and easy to follow. We’d love to hear your feedback about what you liked or didn’t like about this part of the Tutorial.
Use the “Was this doc helpful to you?” form at the bottom of this page to let us know what worked well and what we can improve.
What’s coming next?
Right now, all your blog posts and their excerpts are being rendered in one long page. It would be better if each post lived on its own page, and then the Blog page could link out to all the different posts.
In Part 6, you’ll learn how to use Gatsby’s filesystem route API to dynamically create new pages for each of your blog posts.
Continue to Part 6